The biography of Elon Musk, written by Walter Isaacson, spans nearly 700 pages and was released in September 2023.
Isaacson has previously authored biographies of Leonardo da Vinci and Steve Jobs.
He spent two years shadowing Musk, attending meetings and texts, and engaging in numerous interviews and late-night conversations to write this book.
The book provides a curated and structured collection of short stories from the life of Elon Musk.
It’s significant and pertinent because it sheds light on the life and work of one of the world’s most influential and controversial businessmen.
In this blog, we will summarize and review the key concepts discussed in the book.
We will also discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the book and provide information on where to find the PDF version of the book.

Elon Musk by Walter Isaacson
Publication Date: August 12, 2023
Publisher: Simon & Schuster UK
Page Count: 680 pages
Publication Format: Print Book, Kindle, Audiobook
Edition: N/A
Series: N/A
Average Rating On Amazon: 4.7 out of 5 stars
Average Rating On Goodread: 4.5 out of 5 stars
ISBN13: 978-1398527492
ASIN: B0BW9V7KTY
Author Walter Isaacson: Website, Twitter, Goodreads
Genres: Biography, Nonfiction, Business, Technology, Biography Memoir Self Help, Personal Development

- Elon Musk Book Summary With Table Of Content
- Chapter Wise Book Summary Of Elon Musk by Walter Isaacson
- PROLOGUE: Muse of Fire
- Chapter 1: Adventurers
- Chapter 2: A Mind Of His Own (Pretoria, the 1970s)
- Chapter 3: Life with Father (Pretoria, the 1980s)
- Chapter 4: The Seeker (Pretoria, the 1980s)
- Chapter 5: Escape Velocity (Leaving South Africa, 1989)
- Chapter 6: Canada (1989)
- Chapter 7: Queen’s (Kingston, Ontario, 1990–1991)
- Chapter 8: Penn (Philadelphia, 1992–1994)
- Chapter 9: Go West (Silicon Valley, 1994–1995)
- Chapter 10: Zip2 (Palo Alto, 1995–1999)
- Chapter 11: Justine (Palo Alto, the 1990s)
- Chapter 12: X.com (Palo Alto, 1999–2000)
- Chapter 13: The Coup (PayPal, September 2000)
- Chapter 14: Mars (SpaceX, 2001)
- Chapter 15: Rocket Man (SpaceX, 2002)
- Chapter 16: Fathers and Sons (Los Angeles, 2002)
- Chapter 17: Revving Up (SpaceX, 2002)
- Chapter 18: Musk’s Rules for Rocket-Building (SpaceX, 2002–2003)
- Chapter 19: Mr. Musk Goes to Washington (SpaceX, 2002–2003 Gwynne)
- Chapter 20: Founders (Tesla, 2003–2004)
- Chapter 21: The Roadster (Tesla, 2004–2006)
- Chapter 22: Kwaj (SpaceX, 2005–2006)
- Chapter 23: Two Strikes (Kwaj, 2006–2007)
- Chapter 24: The SWAT Team (Tesla, 2006–2008)
- Chapter 25: Taking the Wheel (Tesla, 2007–2008)
- Chapter 26: Divorce (2008)
- Chapter 27: Talulah (2008)
- Chapter 28: Strike Three (Kwaj, August 3, 2008)
- Chapter 29: On the Brink (Tesla and SpaceX, 2008)
- Chapter 30: The Fourth Launch (Kwaj, August–September 2008)
- Elon Musk By Walter Isaacson Book Reviews
- Download Elon Musk Ebook
- Listen Elon Musk By Walter Isaacson Audiobook
- Download Elon Musk By Walter Isaacson Free PDF
Elon Musk Book Summary With Table Of Content
- PROLOGUE: Muse of Fire
- Chapter 1: Adventurers
- Chapter 2: A Mind Of His Own (Pretoria, the 1970s)
- Chapter 3: Life with Father (Pretoria, the 1980s)
- Chapter 4: The Seeker (Pretoria, the 1980s)
- Chapter 5: Escape Velocity (Leaving South Africa, 1989)
- Chapter 6: Canada (1989)
- Chapter 7: Queen’s (Kingston, Ontario, 1990–1991)
- Chapter 8: Penn (Philadelphia, 1992–1994)
- Chapter 9: Go West (Silicon Valley, 1994–1995)
- Chapter 10: Zip2 (Palo Alto, 1995–1999)
- Chapter 11: Justine (Palo Alto, the 1990s)
- Chapter 12: X.com (Palo Alto, 1999–2000)
- Chapter 13: The Coup (PayPal, September 2000)
- Chapter 14: Mars (SpaceX, 2001)
- Chapter 15: Rocket Man (SpaceX, 2002)
- Chapter 16: Fathers and Sons (Los Angeles, 2002)
- Chapter 17: Revving Up (SpaceX, 2002)
- Chapter 18: Musk’s Rules for Rocket-Building (SpaceX, 2002–2003)
- Chapter 19: Mr. Musk Goes to Washington (SpaceX, 2002–2003 Gwynne)
- Chapter 20: Founders (Tesla, 2003–2004)
- Chapter 21: The Roadster (Tesla, 2004–2006)
- Chapter 22: Kwaj (SpaceX, 2005–2006)
- Chapter 23: Two Strikes (Kwaj, 2006–2007)
- Chapter 24: The SWAT Team (Tesla, 2006–2008)
- Chapter 25: Taking the Wheel (Tesla, 2007–2008)
- Chapter 26: Divorce (2008)
- Chapter 27: Talulah (2008)
- Chapter 28: Strike Three (Kwaj, August 3, 2008)
- Chapter 29: On the Brink (Tesla and SpaceX, 2008)
- Chapter 30: The Fourth Launch (Kwaj, August–September 2008)
Chapter Wise Book Summary Of Elon Musk by Walter Isaacson
PROLOGUE: Muse of Fire
Elon Musk’s childhood in South Africa was filled with adversity. His early years were filled with bullying and harrowing experiences, both at school and at a wilderness survival camp.
Musk was a victim of violence, both in the world and at home, his father’s volatile ways affecting him deeply.
But this troubled past also made him prone to drama in his personal and professional life. Despite the emotional trauma, Musk’s determination has propelled him to unprecedented accomplishments in the fields of technology and space.

Chapter 1: Adventurers
Elon Musk’s inclination towards risk was inherited from his maternal grandfather, Joshua Haldeman, a Canadian adventurer. He was actively involved in the Social Credit Party and the Technocracy movement.
The family earned the nickname “The Flying Haldemans” due to their aviation adventures. In 1950, they moved to South Africa, with Haldeman being attracted to tales of a “lost city” in the Kalahari Desert.
The family mantra became “Live dangerously—carefully.” Tragically, Haldeman died in a flight accident when Elon was just three.
Maye, Elon’s mother, emerged as a blend of beauty and brains, engaging in modeling from a young age. After a tumultuous courtship, she married Errol Musk, an engineer and pilot.
Their relationship was fraught with infidelity and disagreements. Despite the troubled relationship, the couple’s union led to the birth of Elon Musk.
Know More: 50 Best Self Help Books Of All Time
Chapter 2: A Mind Of His Own (Pretoria, the 1970s)
Elon Musk was born to Maye and Errol Musk on June 28, 1971. At first, they wanted to call him “Nice,” but they decided to call him “Elon Reeve”. He has two siblings, Kimbal and Tosca.
As a precocious but socially awkward child, he taught himself computer programming and read books. His parents divorced when he was 8; he lived with his mother but visited his father on weekends.

Chapter 3: Life with Father (Pretoria, the 1980s)
At ten years old, Elon decided to live with his father. He wanted to spend time with his lonely dad and his grandma, who thought it was unfair that Elon’s mom had all the kids.
However, Elon later regretted the decision, describing his father as “horrible.” Despite their challenging relationship, Elon’s early years with Errol were filled with adventures, from building a lodge to participating in hunting.
Elon was both academically gifted and dreamy, often engrossed in reading or experiments. Elon became interested in space and technology by reading books and encyclopedias. This made him think about becoming a tech mogul in the future.
Chapter 4: The Seeker (Pretoria, the 1980s)
As a child, Elon Musk questioned religion and sought the meaning of life through reading. He loved sci-fi like Asimov’s Robots and Heinlein’s The Moon is a Harsh Mistress, which inspired his interest in space travel and AI protecting humanity.
Douglas Adams’ Hitchhiker’s Guide to the Galaxy also profoundly influenced Musk’s thinking.
At 11, Musk saw a computer for the first time, leading to a lifelong passion. He quickly learned programming, created a video game named Blaster at 13, and began selling games.
Chapter 5: Escape Velocity (Leaving South Africa, 1989)

At 17, Elon realized that he had to escape the verbal abuse of his unstable father. Errol Musk’s mood swings and rants questioning reality tortured his sons psychologically.
In 1989, shortly before turning 18, Elon obtained a Canadian passport and a one-way ticket out of South Africa against his father’s wishes.
Chapter 6: Canada (1989)
With $4k from parents, he backpacked, wandered by bus, and did farm work. When his luggage was lost, Musk realized that the financial system had problems.
He then did gritty labor in Vancouver before reuniting with his mother and sister in Toronto.
Elon, a recluse, frequently observed his outgoing sister Tosca, even at social gatherings, while also maintaining a reading habit.
Chapter 7: Queen’s (Kingston, Ontario, 1990–1991)
Elon Musk didn’t do very well on his college SAT tests. He got 670 in the verbal section and 730 in the math section. At Queen’s University, Elon Musk made his first real friend, Navaid Farooq.
Elon mastered a business strategy game at Queen’s, revealing his analytical prowess.
He enjoyed late-night philosophy talks and strategy games with Farooq. Their favorite games were “Civilization” and “Warcraft,” with Musk saying that he had a strategic mind.
After impressing Peter Nicholson from Scotiabank, Musk got a summer job. He proposed an idea related to “Brady Bonds” to profit from Latin American debt, but the bank declined.
This experience gave Musk a skeptical view of traditional finance and seeded the idea for PayPal. He realized he disliked working under others.

Chapter 8: Penn (Philadelphia, 1992–1994)
Bored at Queen’s, Elon Musk transferred to UPenn in 1992.
Elon’s passion for technology and a desire to be free from his traditional business-minded bosses led him to major in physics and business at Penn.
Musk immersed himself in physics studies, particularly with his friend Robin Ren. Musk’s ambitions included rockets to Mars, promoting electric vehicles, and championing solar energy. His senior paper praised his vision of a future power station in space.
Contrary to his reserved nature, Musk explored partying at Penn. With friend Adeo Ressi, he co-hosted elaborate parties in a rented house, attracting hundreds of attendees.
While he enjoyed the party atmosphere, Musk stayed sober, often overseeing the events.
Chapter 9: Go West (Silicon Valley, 1994–1995)
In the 1990s, Ivy League students were often pulled towards Wall Street or Silicon Valley. Elon Musk didn’t really like finance, but he liked Silicon Valley a lot.
At Penn, Musk interned at Pinnacle Research Institute, studying a potentially groundbreaking “supercapacitor” and at Rocket Science.
Musk had a keen interest in hardware, especially cars, unlike many techies of his time. He changed a four-speed BMW into a five-speed one, hinting at what he might do with cars in the future.
Chapter 10: Zip2 (Palo Alto, 1995–1999)
1995, Elon and Kimbal Musk founded Zip2, merging online maps and business listings.
Though initially met with skepticism, they persevered, often facing hardships such as sleeping in their office. Their dedication and timely investments from family led Zip2 to succeed in partnering with major newspapers.
1999 Compaq Computer acquired Zip2 for $307 million, transforming Elon and Kimbal into multi-millionaires At age 27.

Chapter 11: Justine (Palo Alto, the 1990s)
At Queen’s University, Elon Musk began dating fellow student Justine Wilson. Musk’s family, especially his brother and mom, didn’t like her. Yet, Musk remained captivated, leading to a romantic proposal.
Their relationship was filled with drama; both found energy in their disputes. A trip to Paris saw a heated debate on Christian symbolism. As their wedding neared, concerns grew.
Musk’s prenuptial agreement made things even more stressful. Thriving on drama, the combative couple fought vigorously. Justine reluctantly signed a prenup just before their wedding.
Chapter 12: X.com (Palo Alto, 1999–2000)
After selling Zip2, Musk founded the online financial services company X.com in 1999 with $12 million of his fortune, seeking to disrupt banking.
Despite squabbles with staff, X.com launched an online payment feature that proved very popular.
The platform’s feature allowing money transfers via email became unexpectedly popular, especially among eBay users. Around the same time, a similar service called PayPal, founded by Peter Thiel and Max Levchin, was gaining traction.
Negotiations between the two companies were intense, but eventually, they merged, and PayPal became the dominant brand.
Chapter 13: The Coup (PayPal, September 2000)
In the early 2000s, PayPal became a source of tension for senior company members. Max Levchin, one of the co-founders, felt that Musk was dismissive of critical issues like fraud.
Peter Thiel and Luke Nosek, who shared a similar sentiment, initiated a clandestine campaign to emphasize the significance of the PayPal brand over X.com.
When Musk went on a belated honeymoon in September, a coalition was formed to replace him with Thiel. Despite his efforts to salvage the situation, the board voted him out.
Even though he was initially upset, Musk later said that leaving PayPal would let him work on bigger projects like SpaceX and Tesla.

Chapter 14: Mars (SpaceX, 2001)
After being ousted from PayPal, Elon Musk took up flying lessons, reminiscent of his family history. He received his pilot’s license after an intense 2-week training period.
Musk was shocked that NASA had no plans for Mars, so he committed to colonizing space. He saw the colonization of other planets as essential for three reasons:
- To ensure the continuous evolution of technology,
- safeguard human civilization from Earth-bound threats, and
- rekindle the spirit of adventure.
He moved to Los Angeles to be closer to aerospace companies and started building a rocket engineering team. With Jim Cantrell’s help, Musk traveled to Russia to buy an affordable rocket for his Mars missions.
Chapter 15: Rocket Man (SpaceX, 2002)
During a trip to Moscow, Elon Musk and his companions aimed to buy a used Russian rocket for a mission to Mars. Despite the cultural misunderstandings and hard negotiations, a Russian official faced steep rocket prices.
Frustrated, Musk realized rockets were overpriced based on their component costs. On his way back, he crunched numbers and thought he could build a rocket himself. This led to the formation of SpaceX.
Initially, friends tried to dissuade him, showing rockets exploding, but Musk was determined. He wanted to make rockets that were cheap enough to help space exploration.

Chapter 16: Fathers and Sons (Los Angeles, 2002)
In May 2002, as Elon Musk was launching SpaceX, his son Nevada was born. Tragically, at ten weeks old, Nevada succumbed to Sudden Infant Death Syndrome.
While Musk coped with Nevada’s death silently, Justine expressed her grief openly. Elon found it hard to discuss the tragedy, but Justine thought he was feeling emotional because of his difficult childhood.
Chapter 17: Revving Up (SpaceX, 2002)
From rural Idaho, Tom Mueller was fascinated by rockets as a child, frequently building and destroying model ones.
After studying, he joined TRW, the company responsible for the moon landing rocket engine. There, he developed the world’s most powerful amateur rocket engine.
In 2002, Elon Musk learned of Mueller’s expertise. The rocket they were developing was named Falcon 1, and its engines were dubbed Merlin and Kestrel by Mueller.

Chapter 18: Musk’s Rules for Rocket-Building (SpaceX, 2002–2003)
Musk was determined to reduce costs wherever possible. Instead of relying on external suppliers, Musk preferred to manufacture components in-house.
This helped SpaceX control costs and avoid relying too much on other suppliers, who might charge more or take longer to deliver things.
Musk’s most standout attribute is his tendency to question established norms and practices. He pushed his engineers to think critically about every “requirement” and didn’t accept generic answers.
This way, he encouraged first-principles thinking—a method of reasoning from fundamental truths rather than by analogy or accepted norms.
Chapter 19: Mr. Musk Goes to Washington (SpaceX, 2002–2003 Gwynne)
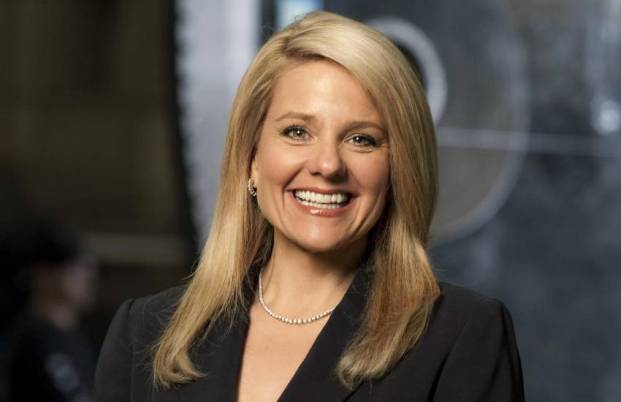
Elon Musk is known for his challenging leadership style and reluctance to share power. Yet, Gwynne Shotwell, who joined SpaceX in 2002, is an exception to this pattern.
They’ve worked side by side for over two decades. Shotwell is honest and can talk to Musk without making him upset.
She understands Musk’s focus on the mission and often acts as a mediator in the company. Shotwell plays a pivotal role in SpaceX’s interactions with institutions like NASA.
Musk’s risk-taking approach led to a lawsuit against NASA over a contract, which SpaceX ultimately won.
Chapter 20: Founders (Tesla, 2003–2004)
JB Straubel, an electric vehicle enthusiast, introduced Musk with AC Propulsion’s tzero prototype. Even though AC’s founders would rather not sell it, the test drives convinced Musk that a high-end electric sports car could change people’s minds.
The co-founders of Tesla, Eberhard, and Tarpenning, also aimed for an electric roadster.
Musk made a key investment and became Tesla’s chairman. He urged partnership with Straubel, bonding the five co-founders over their shared mission.
Chapter 21: The Roadster (Tesla, 2004–2006)
Unlike the auto industry norms, Musk insisted that Tesla controls its destiny by vertically integrating, producing its own components instead of relying on suppliers. But Tesla started by putting together Roadsters from suppliers like Lotus.
As Musk got more involved in the Roadster’s design against Eberhard’s warnings about cost, his relentless push for beauty and performance additions kept raising the price.
Musk’s vision made the Roadster a lust-worthy, perception-changing electric car. Musk obsessively redesigned parts like the doors and headlights for beauty despite warnings on costs.

Chapter 22: Kwaj (SpaceX, 2005–2006)
Elon Musk’s SpaceX had to move to Kwajalein Atoll in the Marshall Islands to launch its rockets because the Air Force took too long to approve their use of Vandenberg Air Force Base.
The location of Kwaj was far away and unsuitable, but it was the only option they had at the time. The SpaceX team on Kwaj was resourceful and innovative, and they developed ways to save money and get the job done.
For example, they built a wheel cradle to transport the rocket between the hangar and the launchpad instead of paving the path.
Chapter 23: Two Strikes (Kwaj, 2006–2007)
Elon Musk’s SpaceX launched its first Falcon 1 rocket on March 24, 2006, from Kwajalein Atoll in the Marshall Islands. The launch failed 25 seconds after liftoff due to a fuel leak caused by a corroded B-nut.
SpaceX learned from its mistake and became more cautious in its approach to testing and manufacturing.
SpaceX’s second launch attempt, in March 2007, was successful until the second stage began to wobble and eventually crashed back to Earth.
Musk learned from this second failure and said, “From now on, we are going to have eleven items on our risk list, never just ten.”

Chapter 24: The SWAT Team (Tesla, 2006–2008)
In 2007, Tesla faced severe production problems with the Roadster, which caused costs to balloon and hundreds of issues that caused delays. Elon Musk made unilateral moves, like visiting Lotuss factory, which hurt his relationship with CEO Eberhard.
The problems with the Roadster were due to technical difficulties with the transmission, which caused delays and recalls.
The first prototype was faulty, and the car weighed 60% more than an Elise, causing production costs to be higher than expected.
Chapter 25: Taking the Wheel (Tesla, 2007–2008)
After revealing production nightmares, Martin Eberhard offered to step down as Tesla CEO in 2007. However, no replacement was found, so Elon Musk abruptly ousted Eberhard before a successor was lined up. This move caused Eberhard to feel betrayed, sparking enduring animosity between the two.
Interim CEO Michael Marks emphasized cash flow and resisted Musk’s treatment of staff, resulting in clashes over Musk’s authoritarian approach.
Marks advocated outsourcing assembly, which violated Musk’s vision. After Marks quit, Musk finally took the CEO role in 2008.

Chapter 26: Divorce (2008)
Justine and Elon Musk had a tumultuous relationship that was filled with fights and lavish living. They had a son named Nevada, who died of SIDS in 2002, and they went on to have twins and triplets through IVF.
Even though they were rich and successful, Justine felt that Elon was addicted to stress and that she was turning into a “trophy wife.” She tried to get him to go to therapy, but he resisted.
She told Elon that their relationship needed to change. After a month of counseling, Elon gave Justine an ultimatum to accept the marriage or he would divorce her. He asked for a divorce When she said things were going wrong.

Chapter 27: Talulah (2008)
After breaking up with his first wife, Justine, Elon Musk met Talulah Riley, an English actress, in July 2008, after breaking up with her. They met at a nightclub in London, and Musk was immediately smitten.
They spent the next three days together, and by the end of the trip, Musk had proposed. Riley accepted, and they were married two years later.
Musk’s parents were initially skeptical of the relationship but eventually approved of Riley. She was intelligent, funny, and successful; her parents were kind and down-to-earth.
Musk and Riley’s relationship was passionate and intense, but it was also volatile. They divorced twice but always found their way back to each other.
Chapter 28: Strike Three (Kwaj, August 3, 2008)
Elon Musk was determined to make SpaceX a success, even after three unsuccessful launches of the Falcon 1 rocket. He risked everything on the fourth launch, and it paid off.
The Musk team redesigned the cooling system for the Merlin engine. This caused the problem that led to the previous failures.
Musk’s optimism and determination inspired his team to keep working hard, even when things were tough. The fourth launch was a success, and SpaceX was now a big player in the space industry.

Chapter 29: On the Brink (Tesla and SpaceX, 2008)
Elon Musk was in a desperate situation in 2008. Tesla ran out of money, and SpaceX had yet to get a rocket into orbit. Musk borrowed money from friends and family to keep Tesla afloat; even regular Tesla employees wrote checks. He also worked tirelessly, day and night, to try to save both companies.
Musk’s friends and colleagues urged him to choose between Tesla and SpaceX, but he refused. He said he couldn’t bear to give up on either company and was determined to save both.
Musk’s perseverance and determination paid off. In 2009, Tesla received a $465 million loan from the U.S. Department of Energy, and SpaceX secured a $1.6 billion contract with NASA.
Both companies became successful and influential leaders in their respective industries.
Chapter 30: The Fourth Launch (Kwaj, August–September 2008)
On September 28, 2008, the fourth Falcon 1 launch succeeded in reaching orbit, becoming the first privately built rocket to do so.
It was a major milestone that saved entrepreneurial space efforts and led NASA to have a commercial cargo competition, which SpaceX won with a $1.6 billion contract in late 2008.
After the success, Musk made Gwynne Shotwell SpaceX President to partner with him. He would focus on engineering, and she would handle business aspects.

If you'd like to read the complete book summary of "Elon Musk," please let me know in the comments, and I'll happily provide it for you.
Elon Musk By Walter Isaacson Book Reviews
- Isaacson weaves biographies like no one else. His biography of Steve Jobs was iconic. And this time around, he kept up. Musk is a dynamic personality, as is Isaacson, who raises his stature to new heights yet never pulls a blow when highlighting his shortcomings. A perfectly balanced, awe-inspiring, and thrilling sliver on Musk. Must read. Dot.
- Thanks to Walter Isaacson for this gem of a book. I would highly recommend it to Elon fans curious to know how his brain works.
- Amazing insight into Musk’s thinking and genius. A must-read for any entrepreneur. No one can be as crazy as him, but he needs at least 70% to succeed as an entrepreneur.
- Whatever you think of Mr. Musk, he is a man worth understanding— which makes this a book worth reading.” — The Economist
- “With Elon Musk, Walter Isaacson offers both an engaging chronicle of his subject’s busy life so far and some compelling answers…” — Wall Street Journal
- “An experienced biographer’s comprehensive study.” —The Observer
- “Walter Isaacson’s all-access biography… Its portrait of the tech maverick is fascinating.” —The Telegraph
- “Isaacson boils Musk down to two men… the result is a beat-by-beat book that follows him insider important rooms and explores obscure regions of his mind.” —The Times
- Amazing book. Walter Isaacson presents a 360-degree picture of Musk’s life and he makes the reader realise why Elon Musk does what he does.
- Amazing biography. i wouldn’t consider myself a fan of Elon, but this biography was way better than the Ashlee Vance one
- Isaacson has done it again—a superb biography of a genius. One with world-changing talent and drive and enough faults for ten men. Very thorough and revealing. Read it immediately!
- I enjoyed reading this book, Isaacson is a skilled and proven author; there are many fascinating stories and anecdotes.
Download Elon Musk Ebook
Listen Elon Musk By Walter Isaacson Audiobook
Try Free Audible Premium Plus and Get Up to Two Free Audiobooks
Download Elon Musk By Walter Isaacson Free PDF
If you’re an entrepreneur, an investor, or simply someone who is curious about the future, then you should read Elon Musk by Walter.
This book is a must-read for anyone who wants to understand the mind of one of the world’s most successful and influential people.
You can get a copy of the book on Amazon. However, be careful not to fall for scams offering free copies of the book (pdf), as it may be illegal and potentially harmful to your device or personal information.
If you’re not able to purchase a copy of the book, there are still many ways to learn about Elon Musk and his business philosophy. You can read online articles and watch educational videos on YouTube. You can also find free resources at your local library or institution.
You can also read our blog for Downloading Free PDF book Websites Like Z-Library (Top 10 Alternatives)
If you are serious about investing in your personal development, you may want to consider exploring these options as well.